Access and use
Make sure you have a basic understanding of the policies and procedures that regulate access and fair and equitable sharing of the benefits arising from the utilization of CWR, and clearly describe all details in the management plan of your genetic reserve.
Discuss how policies and procedures for access, use and benefit sharing from use will be applied when samples from the genetic reserve are backed-up ex situ in genetic resources centres and made available to users under standard access and benefit sharing by the genebank on behalf of the genetic reserve.
Policies for regulating access and use of CWR
The access and use of CWR species are critical to meeting the global goals of food and nutritional security and need to be facilitated so that the benefits that CWR provide may be realized.
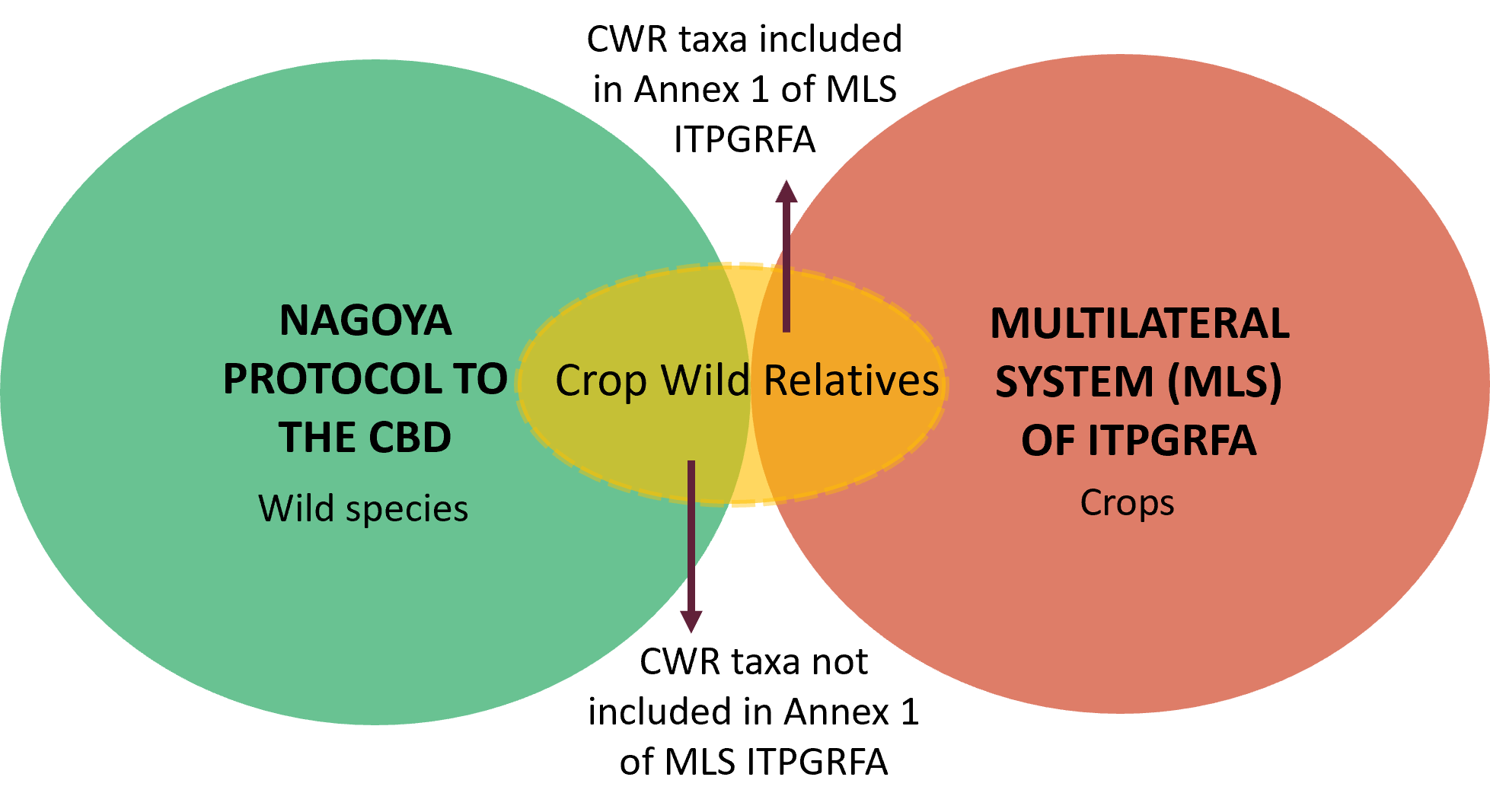
The Nagoya Protocol to the CBD, which came into force into 2014, and the relevant EU Regulation (511/2014), state specific obligations for users of genetic resources related to the fair and equitable sharing of the benefits arising out of the utilization.
On the other hand, access and benefit sharing to some CWR species of crops are governed by the International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture (ITPGRFA), which establishes a multilateral system of access and benefit sharing (article 10). The Treaty, through its article 12, requires that contracting parties facilitate access to plant genetic resources for food and agriculture under the multilateral system as defined in article 11. This includes PGRFA that are listed under Annex 1 (which includes specific CWRs) of the Treaty and that are under the management and control of the contracting party and in the public domain.
Many countries have already developed their own procedures for ensuring access and use of plant genetic resources for food and agriculture, and wild plants, both including CWR species.